
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Advanced Photonics Center, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Light Manipulations and Applications, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250358, China
Photonic structures with topological edge states and resonance loops are both important in optical communication systems, but they are usually two separate structures. In order to obtain a photonic system combining properties from both, we design multiple-layer nested photonic topological structures. The nested topological loops not only have topological protection immune to structural disorder and defects, but also possess both the properties of unidirectional propagation and loop resonance. Through mode analysis and simulations, we find that the transport can form diverse circulation loops. Each loop has its own resonance frequencies and can be solely excited in the nested layered structure through choosing its resonance frequencies. As a result, this work shows great application prospects in the area of reconfigurable photonic circuits.
topological edge states unidirectional propagation loops resonance reconfigurability Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(6): 061301
1 南开大学 电子信息与光学工程学院 现代光学研究所,天津300350
2 天津市微尺度光学信息技术科学重点实验室,天津,300350
3 天津市光电传感器及传感网络技术重点实验室,天津,0050
4 上海工程技术大学 数理与统计学院,上海201620
5 南京师范大学 计算机与电子信息学院,南京210023
6 东南大学 先进光子学中心,南京21009
7 山东师范大学 光场调控与应用协同创新中心,济南250358
基于麦克斯韦应力张量理论,对多边形金纳米粒子在聚焦场下的光力特性进行了研究。以三角形金纳米粒子为例,从粒子在聚集场中的受力情况出发,分别研究了具有圆对称能量分布的聚焦场和具有三角形能量分布的聚焦场对三角形金纳米粒子的捕获特性。研究结果表明,当使用圆对称聚焦场时,可对边长为50~350 nm的三角形金纳米粒子实现稳定捕获;当使用三角形聚焦场时,在粒子以和聚焦场形状匹配的角度进入聚焦场的情况下,可对边长为100~350 nm的三角形金纳米粒子实现稳定捕获。将圆对称聚焦场和三角形聚焦场对三角形金纳米粒子的捕获特性进行比较,发现三角形聚焦场在x方向的捕获力要强于圆对称聚焦场;而在y方向,三角形聚焦场对粒子的捕获范围要大于圆对称聚焦场。该工作研究了三角形的金属纳米粒子在不同形状聚焦场下的光力捕获特性,为基于非球形金属粒子的光学操纵在拉曼光谱超分辨成像、粒子微加工等领域的应用奠定了理论基础。
光镊 三角形金纳米粒子 径向矢量光场 紧聚焦 光力 Optical tweezers Triangular gold nano-particles Radially polarized beam Tightly focusing Optical force
东南大学 先进光子学中心,江苏 南京 210096
具有偏振结构分布的强激光与非线性光学材料相互作用导致了多种新颖的非线性光学效应,反映了材料的非线性光学特性,调制了光场的传播行为。笔者概述了矢量光场激发三阶非线性光学效应的研究进展。首先简要介绍了任意偏振光激发三阶非线性光学效应的理论,如非线性薛定谔方程、光束传播方程、各向同性和各向异性三阶非线性光学系数。也简要介绍了表征三阶非线性光学系数的 Z-扫描技术。在弱聚焦条件下,给出了诸如径向偏振光、杂化偏振光和柠檬型庞加莱光束这三种类型矢量光场的焦场表达式。其次,重点回顾了多种矢量光场激发的各向同性/各向异性三阶非线性光学效应,包括径向偏振光激发的各向异性非线性光学效应、杂化偏振光激发的各向同性和各向异性非线性光学效应、柠檬型庞加莱光束激发的各向同性/各向异性非线性光学效应。最后,简要讨论了矢量光场在非线性偏振旋转、光束整形、可控光场塌缩与成丝和光限幅方面的应用。
矢量光场 非线性折射 双光子吸收 各向同性 各向异性 vectorial light field nonlinear refraction two-photon absorption isotropy anisotropy 红外与激光工程
2020, 49(12): 20201050

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Advanced Photonics Center, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
2 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology of Jiangsu Province, School of Physical Science and Technology, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing 210023, China
3 School of Physics and Electronics, Central South University, Changsha 410012, China
4 Collaborative Innovation Center of Light Manipulations and Applications, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250358, China
We investigate femtosecond laser trapping dynamics of two-photon absorbing hollow-core nanoparticles with different volume fractions and two-photon absorption (TPA) coefficients. Numerical simulations show that the hollow-core particles with low and high-volume fractions can easily be trapped and bounced by the tightly focused Gaussian laser pulses, respectively. Further studies show that the hollow-core particles with and without TPA can be identified, because the TPA effect enhances the radiation force, and subsequently the longitudinal force destabilizes the trap by pushing the particle away from the focal point. The results may find direct applications in particle sorting and characterizing the TPA coefficient of single nanoparticles.
laser trapping multiphoton processes ultrafast nonlinear optics Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(8): 081901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Advanced Photonics Center, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
2 School of Physics and Electronics, Central South University, Changsha 410012, China
Understanding the nonlinear optical effect of novel materials plays a crucial role in the fields of photonics and optoelectronics. Herein, we theoretically and experimentally investigate the simultaneous presence of third-order locally refractive nonlinearity and thermally induced nonlocal nonlinearity saturation. We present analytical expressions for the closed-aperture Z-scan trace and the number of spatial self-phase modulation (SSPM) rings, which allows one to unambiguously and conveniently separate the contributions of local and nonlocal nonlinear refraction in the case that both effects occur simultaneously. As a test, we study both the local and thermally induced nonlocal nonlinear refraction in fullerene/toluene solution by performing continuous-wave Z-scan and SSPM measurements at two different wavelengths. This work enriches the understanding of the physical mechanism of the optical nonlinear refraction effect in solution dispersions of nanomaterials, which can be exploited for nonlinear photonic devices.
190.4420 Nonlinear optics, transverse effects in 190.4870 Photothermal effects Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(6): 061901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Advanced Photonics Center, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
2 Department of Electro-Optics and Photonics, University of Dayton, Dayton, Ohio 45469, USA
3 School of Optical-Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
4 e-mail: cyp@seu.edu.cn
5 e-mail: qzhan1@udayton.edu
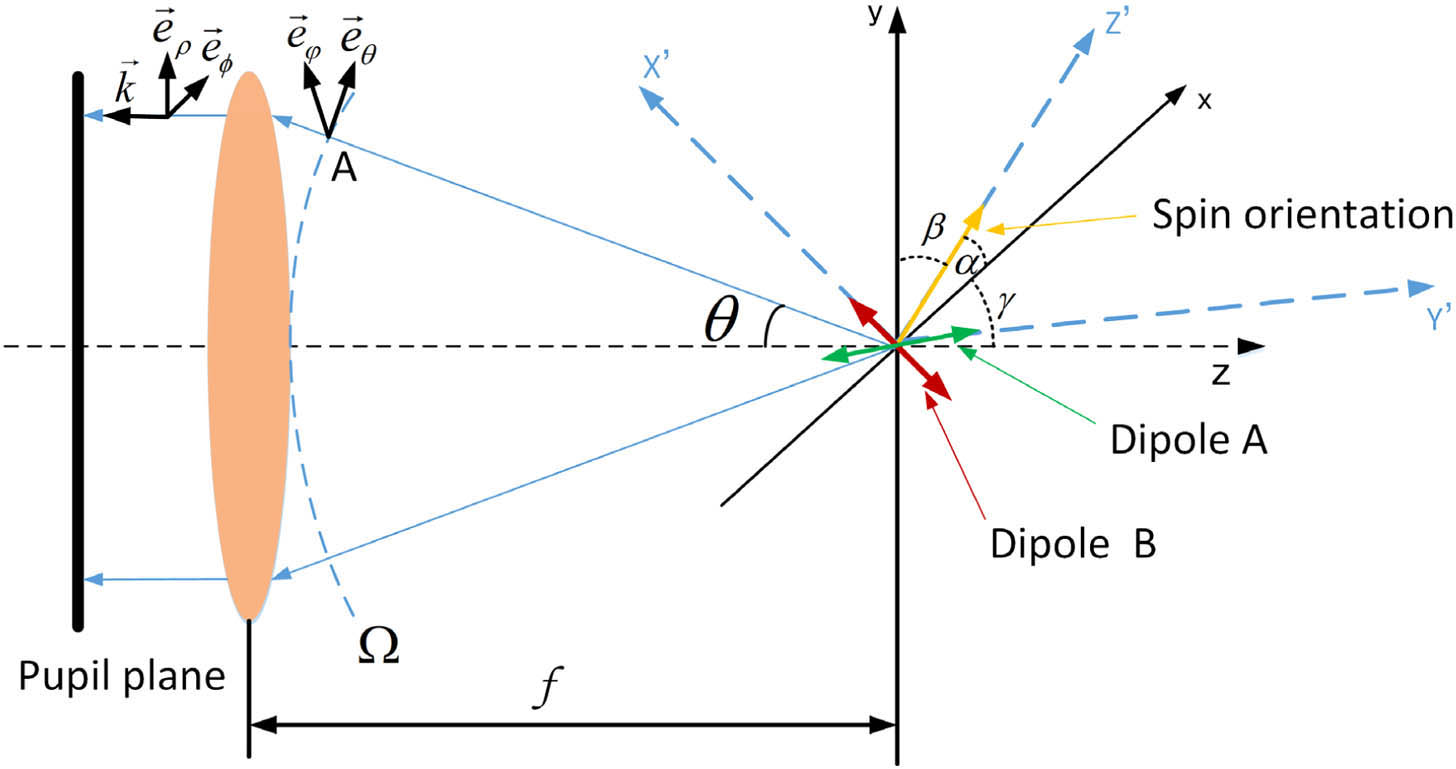
Optical trapping techniques hold great interest for their advantages that enable direct handling of nanoparticles. In this work, we study the optical trapping effects of a diffraction-limited focal field possessing an arbitrary photonic spin and propose a convenient method to manipulate the movement behavior of the trapped nanoparticles. In order to achieve controllable spin axis orientation and ellipticity of the tightly focused beam in three dimensions, an efficient method to analytically calculate and experimentally generate complex optical fields at the pupil plane of a high numerical aperture lens is developed. By numerically calculating the optical forces and torques of Rayleigh particles with spherical/ellipsoidal shape, we demonstrate that the interactions between the tunable photonic spin and nanoparticles lead to not only 3D trapping but also precise control of the nanoparticles’ movements in terms of stable orientation, rotational orientation, and rotation frequency. This versatile trapping method may open up new avenues for optical trapping and their applications in various scientific fields.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(1): 01000069

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Advanced Photonics Center, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, Jiangsu, China
2 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology of Jiangsu Province, School of Physical Science and Technology, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu, China
3 Department of Electro-Optics and Photonics, University of Dayton, 300 College Park, Dayton, Ohio 45469-2951, USA
The principle of optical trapping is conventionally based on the interaction of optical fields with linear-induced polarizations. However, the optical force originating from the nonlinear polarization becomes significant when nonlinear optical nanoparticles are trapped by femtosecond laser pulses. Herein we develop the time-averaged optical forces on a nonlinear optical nanoparticle using high-repetition-rate femtosecond laser pulses, based on the linear and nonlinear polarization effects. We investigate the dependence of the optical forces on the magnitudes and signs of the refractive nonlinearities. It is found that the self-focusing effect enhances the trapping ability, whereas the self-defocusing effect leads to the splitting of the potential well at the focal plane and destabilizes the optical trap. Our results show good agreement with the reported experimental observations and provide theoretical support for capturing nonlinear optical particles.
Kerr effect Laser trapping Particles Ultrafast nonlinear optics Photonics Research
2018, 6(2): 02000138
1 中南大学物理与电子学院, 超微结构与超快过程湖南省重点实验室, 湖南 长沙 410083
2 东南大学电子科学与工程学院先进光子学中心, 江苏 南京 210096
采用Z扫描和泵浦-探测技术研究了GaN薄膜在370 nm时的非线性光学效应和非线性光动力学过程。 首先, 基于GaN薄膜的透射光谱, 结合线性光学理论分析得到了其在370 nm的线性折射率n0、 线性吸收系数α0、 光学带隙Eg等线性光学性质。 采用飞秒激光Z扫描技术, 得到了不同光强激发下的Z扫描实验响应结果, 结合非线性光学理论提取出GaN薄膜可变的光学非线性吸收效应。 在激发光子能量接近GaN带隙情况下, 低光强时材料表现为饱和吸收而高光强时为反饱和吸收, 这是因为低光强下单光子吸收占主导而高光强下以单光子感应自由载流子吸收为主。 闭孔Z扫描测量得到了GaN薄膜的三阶非线性折射系数为n2=-(1.0±0.1)×10-3 cm2·GW-1, 它几乎比传统非线性介质的高出一个数量级。 为了探究上述非线性过程的动力学弛豫时间以及进一步探究GaN薄膜非线性光动力学过程的深层物理机制, 采用了交叉偏振飞秒退相泵浦探测技术观察GaN薄膜的光激发载流子动力学弛豫过程。 实验结果表明, 在低光强下, 饱和吸收效应来源于瞬态单光子吸收, 高光强下单光子感应自由载流子吸收为非瞬态光动力学过程, 其自由载流子弛豫时间约为17 ps。 该工作将为GaN薄膜在紫外非线性纳米器件应用以及GaN薄膜非线性过程的机制分析理解提供新的思路。
GaN薄膜 自由载流子吸收 Z扫描 泵浦-探测 紫外非线性光学 GaN film Free carrier absorption Z-scan Pump-probe Ultraviolet nonlinear optics 光谱学与光谱分析
2017, 37(12): 3781
1 中南大学物理与电子学院 超微结构与超快过程湖南省重点实验室, 湖南 长沙 410083
2 东南大学 先进光子学中心, 江苏 南京 210096
基于飞秒激发Z扫描实验技术, 研究了氮化镓薄膜和不同铝掺杂含量的掺铝氮化镓(以下简称铝镓氮)薄膜的超快非线性光学响应特性。在开孔Z-scan测试中, 纯GaN晶体薄膜表现出典型的双光子吸收特性, 双光子吸收系数为3.5 cm/GW, 且随着激发光强的增大而逐渐减小。随后测试了不同铝掺杂含量的AlxGa1-xN薄膜的非线性吸收系数。结果表明, 随着铝掺杂摩尔分数的提高(0, 19%, 32%, 42%), 非线性吸收系数逐渐减小(18, 10, 6, 5.6 cm/GW)。结合半导体非线性吸收理论分析, AlxGa1-xN薄膜材料的非线性过程主要是双光子吸收主导非线性响应物理过程。实验结果与半导体双光子吸收过程Sheik-Bahae理论符合得很好。
铝镓氮薄膜 双光子吸收 能带调控 AlxGa1-xN films two-photon absorption band-gap engineering
利用红外测温仪、光学测温仪、热电偶测温仪(铂铑-铂)对微波电真空器件用浸渍阴极表面、覆膜阴极表面、阴极侧面(钼筒)进行了温度对比测试研究。结果表明: 采用红外测温仪和光学测温仪测试浸渍阴极表面的温度与采用热电偶测温仪测试的温度相差不大, 而覆膜阴极却相差约50 ℃; 采用红外测温仪和光学测温仪测试阴极侧面(钼筒)的温度相差不大, 都低于热电偶测温仪测试的温度约60 ℃, 这说明红外和光学测试温度值低于阴极的实际温度(热电偶测量值)。由于在阴极表面出现了物理、化学变化, 红外测温仪和光学测温仪测试的阴极表面温度值在1150 ℃左右加热100 min内增加约30 ℃。分析认为这些差异主要是因为覆膜阴极的表面与浸渍阴极的表面及阴极侧面(钼筒)的发射系数不同造成的, 当然测试结果也会随着这些因素的变化而有一定的变化。
微波真空电子器件 热阴极 温度 热辐射 microwave vacuum devices thermal cathode temperature heat radiation 强激光与粒子束
2016, 28(7): 073003





